Australia’s construction industry has been facing significant challenges due to a persistent labor shortage. This issue not only affects the timely completion of projects but also drives up construction costs. This blog explores the extent of the labor shortage, its implications on construction costs, and potential strategies to mitigate these challenges.
The Current State of the Construction Labor Market in Australia
Extent and Causes of the Labor Shortage
The construction sector in Australia has been experiencing a notable labor shortage for several years. The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) reports that job vacancies in Australia’s construction industry hit a peak of 39,000 in 2022, but recent figures indicate a drop to 24,900 by early 2024.
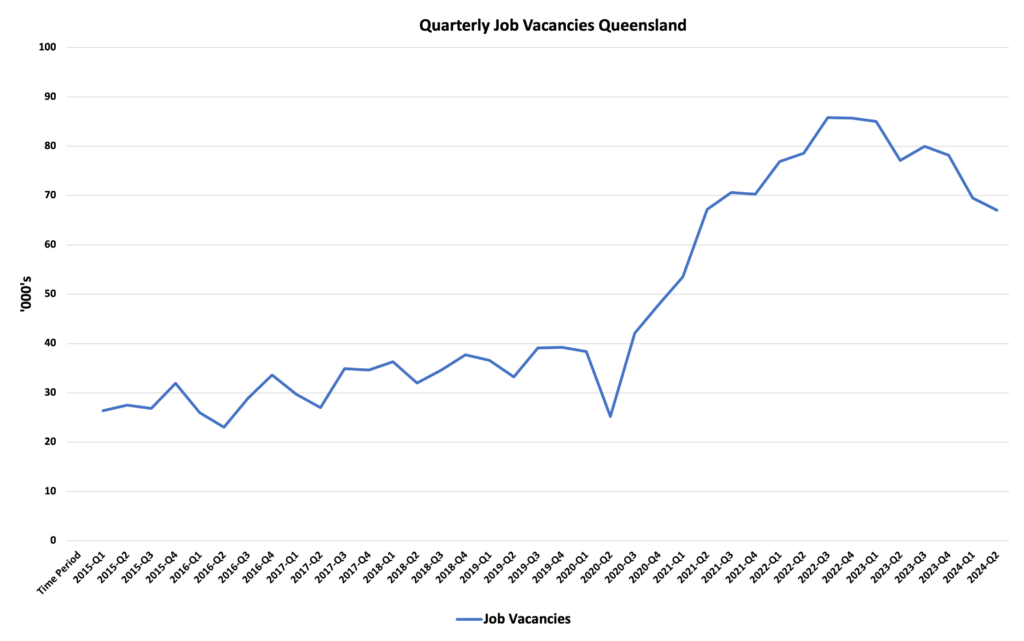
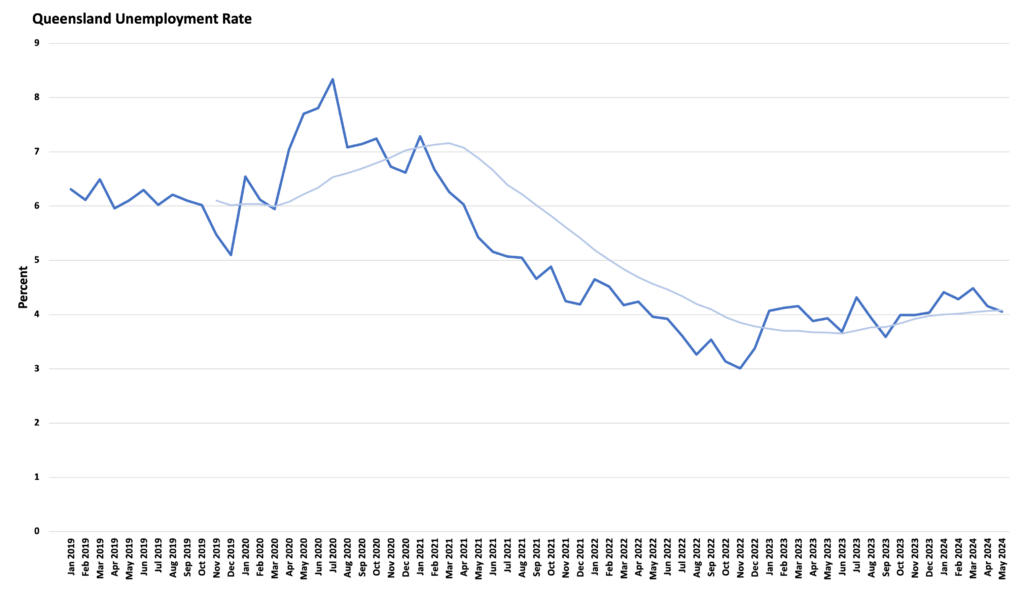
Simultaneously, job vacancies in Queensland have decreased by 20% over the past year, while unemployment has been on the rise. The prospects for those relying on consistently high labor demand seem uncertain, as leading indicators point to a potential slowdown in the upcoming months. Several factors contribute to this shortage:
- Aging Workforce: A significant portion of the construction workforce is nearing retirement age, leading to a decrease in available skilled labor. This demographic shift is a critical factor since it not only reduces the number of workers but also leads to a loss of experienced and highly skilled personnel.
- Insufficient Training and Education: There has been a decline in the number of young people entering construction trades, compounded by inadequate vocational training programs. The existing educational framework does not seem to sufficiently attract or prepare new entrants for the construction industry, further exacerbating the labor shortage.
- Economic Fluctuations and Migration Policies: Economic downturns and stringent migration policies have also played a role in reducing the influx of foreign workers who traditionally fill gaps in the labor market. During periods of economic uncertainty, there is often a decrease in investment in large-scale construction projects, leading to a more volatile labor market.
Regional Variations and Specific Trade Shortages
The labor shortage is not uniform across Australia. Regions such as New South Wales and Victoria, which have seen significant infrastructure development, are particularly hard hit. Additionally, certain trades, including electricians, plumbers, and carpenters, are in higher demand than others.
- Urban vs Rural Disparities: Urban areas tend to have a higher concentration of construction activity, exacerbating labor shortages compared to rural regions. This disparity is due to the concentration of larger infrastructure projects and a higher demand for residential construction in urban centers.
- Specialized Skill Gaps: The demand for specialized skills in new technologies and sustainable construction practices has further strained the labor market. As the construction industry evolves, there is a growing need for workers skilled in areas such as green building technologies, digital construction methods, and complex project management.
Impact of Labor Shortages on Construction Costs
Increased Labor HoSTC
The most direct impact of labor shortages is on labor costs. With fewer workers available, construction companies are forced to offer higher wages to attract and retain skilled labor. The International Construction Market Survey (ICMS) conducted by global professional services consultancy Turner & Townsend assesses construction build, labor costs, and cost inflation across 88 city regions worldwide. Labor shortages continue to be the most significant challenge going forward, with skill deficiencies being felt across all markets.
Delays and Project Overruns
Labor shortages also contribute to project delays and cost overruns. The inability to secure sufficient labor can stall projects, leading to extended timelines and increased costs.
- Extended Project Timelines: Projects frequently run over schedule due to the unavailability of skilled workers, which can lead to penalties and additional costs for construction firms. Delays can disrupt the supply chain, increase financing costs, and reduce the overall efficiency of project execution.
- Cost Overruns: The combination of higher labor costs and extended timelines often results in cost overruns, impacting the profitability and feasibility of construction projects. Cost overruns can lead to renegotiations of contracts, strained relationships with clients, and reduced investor confidence.
- Impact on Quality and Safety: Labor shortages can also affect the quality and safety of construction projects. With fewer skilled workers available, there is a higher risk of substandard work and increased safety incidents (Safe Work Australia, 2023). Ensuring quality and safety in such a scenario often requires additional investments in training and supervision, further driving up costs.
Strategies to Mitigate Labor Shortages and Cost Increases
Enhancing Training and Apprenticeship Programs
Addressing the labor shortage requires a long-term approach focused on training and education. Investing in robust training and apprenticeship programs can help build a pipeline of skilled workers for the future.
- Government Initiatives: Government programs aimed at subsidizing training and apprenticeships can encourage more young people to enter the construction trades. These initiatives can include grants, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships designed to enhance vocational training infrastructure. In 2020-21 and 2021-22, the Australian Government allocated $500 million each year, matched by state and territory governments, to fund approximately 463,000 free or low-cost training placements for job seekers and young people.
- Industry Partnerships: Collaboration between construction companies and educational institutions can ensure that training programs are aligned with industry needs (TAFE NSW, 2023). Industry-specific certifications, hands-on training opportunities, and internships can help bridge the gap between education and employment.
- Promotion of Construction Careers: Campaigns to promote construction careers, highlighting the opportunities and benefits, can attract a new generation of workers. Showcasing success stories and the potential for career advancement can make construction trades more appealing to young people.
Leveraging Technology and Innovation
Innovative technologies can also play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of labor shortages. Automation and advanced construction techniques can help reduce reliance on manual labor.
- Adoption of Automation: The use of automated machinery and robotics can significantly reduce the need for manual labor in certain construction processes (McKinsey & Company, 2023). Technologies such as 3D printing, automated bricklaying robots, and autonomous vehicles can streamline operations and enhance productivity.
- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: These techniques can streamline construction processes, making them less labor-intensive and more cost-effective (Modular Building Institute, 2023). Prefabrication allows for the off-site production of building components, which can then be assembled on-site quickly and efficiently.
- Digital Construction Tools: The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM), project management software, and other digital tools can improve planning, coordination, and execution of construction projects (Construction Industry Development Agency, 2023). These tools enable better resource management, real-time monitoring, and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders.
Policy and Regulatory Reforms
Policy and regulatory reforms can create a more favorable environment for addressing labor shortages and managing construction costs.
- Flexible Immigration Policies: Adjusting immigration policies to allow for easier entry of skilled foreign workers can help alleviate labor shortages (Migration Council Australia, 2023). Temporary work visas and streamlined processing can enable construction companies to quickly respond to labor demands.
- Incentives for Sustainable Practices: Providing incentives for sustainable construction practices can encourage innovation and reduce overall project costs. Government grants and tax credits for green building projects can support the adoption of energy-efficient technologies and materials (Green Building Council of Australia, 2023).
- Streamlined Approval Processes: Simplifying and expediting the approval processes for construction projects can reduce delays and lower administrative costs. Efficient regulatory frameworks can facilitate quicker project initiation and completion (Australian Construction Industry Forum, 2023).
Conclusion
The labor shortage in Australia’s construction industry is a multifaceted issue that significantly impacts construction costs. By understanding the extent of the shortage and its implications, stakeholders can implement strategic measures to mitigate its effects. Enhanced training programs and the adoption of innovative technologies are critical to addressing these challenges and ensuring the sustainable growth of the construction sector.


Leave a Reply to бнанс Реферальний код Cancel reply